When it comes to vegetable gardening, compost is the secret to success. It enriches the soil, provides plants with nutrients, and aids in retaining soil moisture. This tutorial will assist you in understanding compost and in selecting the finest variety for your garden.
Comprehending compost
Organic material that has broken down and been recycled as a soil supplement and fertilizer is known as compost. It serves as the foundation for organic farming and gardening. Because it is nutrient-rich, compost is good for the health of the soil. It improves soil structure, helps soils retain moisture, and gives helpful bacteria a food source.
Collecting organic waste, such as leaves, grass clippings, and kitchen scraps, and allowing it to rot over time is the process of composting. A black, crumbly material that is produced as a result is very effective in enhancing the fertility and health of garden soil. Composting is a great way to improve the fertility and structure of your soil, making it more suitable for planting. To learn more about how to use compost to improve asparagus yield, check out our article on How to Choose Companion Plants for Asparagus.
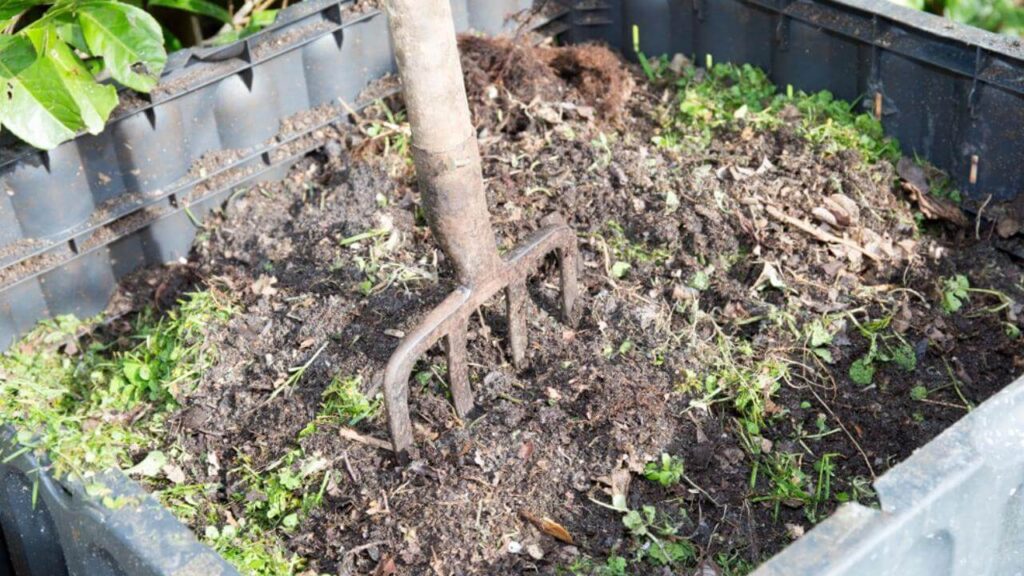

Variety of Compost
You can use many types of compost in your vegetable garden. Every one has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
– Homemade Compost: You may create this compost at home using leftover food and yard trash. Although it is time-consuming to create, it is inexpensive and allows you to recycle your garbage.
– Composted Manure: This type of manure has undergone a composting process to eradicate diseases and weed seeds. Although it is nutrient-rich, if it is not properly composted, certain plants may find it to be too strong.
– Mushroom Compost: This is the compost that is left over after growing mushrooms. Although it can include a lot of salts, it is rich in organic stuff.
Green waste compost is produced using yard waste, such as grass clippings and leaves. Although it is commonly available and reasonably priced, the quality can vary.

Making the Best Compost Choices for Your Vegetable Garden
The finest compost for your vegetable garden will depend on a number of variables. You must take into account your local environment, the type of veggies you are growing, and the state of your soil.
The following advice will help you select the top compost:
– Understand Your Soil: Each type of soil has unique requirements. Clay soils require compost that enhances drainage, whereas sandy soils benefit from compost that provides organic matter and preserves moisture.
– Take into account the plants you have: Some vegetables, such as tomatoes and peppers, enjoy rich, fully decomposed compost. Some crops, like root vegetables, thrive on less fertile compost.
– Verify the Quality: Good compost should have an earthy scent, be crumbly, and be dark in color. Avoid compost that has an offensive odor or that resembles the original waste items.
Use of Compost in Vegetable Gardens
It’s not difficult to use compost in your vegetable garden. Here are the fundamental steps:
– Prepare Your Garden Beds: Before adding compost, clear your garden beds of any weeds or outdated plant life.
– Add compost: Cover your garden beds with a layer that is 2-3 inches thick of compost.
– Use a garden fork or a tiller to incorporate the compost into the top 6 to 8 inches of soil.
– Plant Your Vegetables: Following the mixing of the compost, plant your vegetables as usual.
Do not forget that composting is not a quick fix. To maintain the richness and health of your soil, you should apply compost to your garden beds each year.
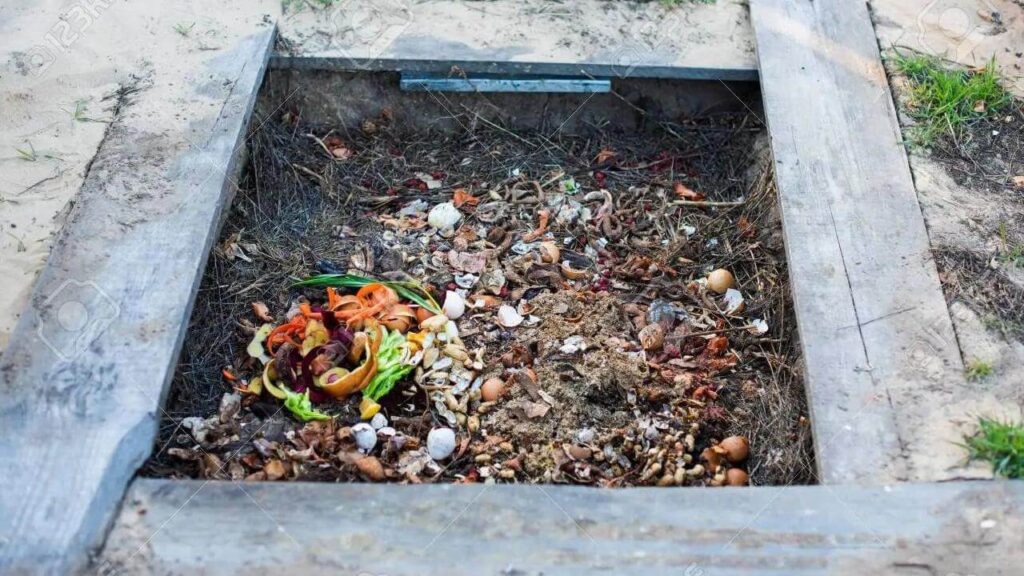

Composting Your Own Food
A fantastic approach to cut waste and produce nutrient-rich soil for your garden is to make your own compost. A quick guide on creating compost at home is provided here:
– Pick a Compost Bin or Pile: You can compost in a jar you buy, a jar you make, or even just a plain pile in a yard corner.
– Gather the Materials for Your Compost: You can compost fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, grass clippings, leaves, and more. Meat, dairy products, and ill plants should not be composted.
– Layer your compost: Begin with a layer of browns (like leaves or straw) for carbon, then add a layer of greens (like vegetable scraps) for nitrogen. Until your container is filled, keep adding layers.
– Turn Your Compost: To ensure that your compost breaks down uniformly, turn it with a shovel or pitchfork every few weeks.
– Put Your Compost to Use: When your compost is crumbly and dark, you can put it to your garden beds.

Composting and crop rotation
Compost plays a significant role in crop rotation, a practice that fosters soil health and disease avoidance. Every year, you may replenish the nutrients your vegetables absorb by adding compost to your garden beds.
One possibility is to plant a light feeder like beans the year after a heavy feeder like tomatoes was planted the year before. If you incorporate compost into your soil annually, it will have an abundance of nutrients for whatever you plant.
Conclusion
As the first step toward a profitable and healthy growing season, select the best compost for your vegetable garden. The greatest compost, whether homemade or purchased, is the one that meets the demands of your soil and plants.



Leave a Comment